Responding To Web Application VAPT Results: A Comprehensive Guide
💡 In the Panama Papers scandal of 2016, where a collection of 11.5 million records from the Panamanian law firm Mossack Fonseca were leaked, it was revealed how wealthy people like politicians, celebrities, and business leaders, misused offshore tax havens to avoid paying taxes, launder money, and engage in other illegal actions.
However, one might wonder why this major data breach actually occurred. It’s because the firm’s website was hosted on outdated software and did not have the necessary measures to filter, validate or sanitise users’ inputs. Such loopholes can allow attackers to execute unintended commands and gain access to sensitive data by injecting malicious data as part of a command or query.
This vulnerability in the software could easily have been detected in a VAPT assessment, saving the firm from the disastrous consequences of the data breach.
Once your organisation executes a VAPT, it is followed by a comprehensive report detailing the identified vulnerabilities, their severity levels, and potential remediation steps.
However, for many organisations, deciphering this report and translating its findings into actionable steps can be a challenge.
Through this blog, we aim to equip you with the knowledge to interpret and act on the results of a web application VAPT report efficiently.
Understanding a VAPT Report
Before we dive into the interpretation of a VAPT report, you must know the different sections that a well-structured VAPT report typically includes:
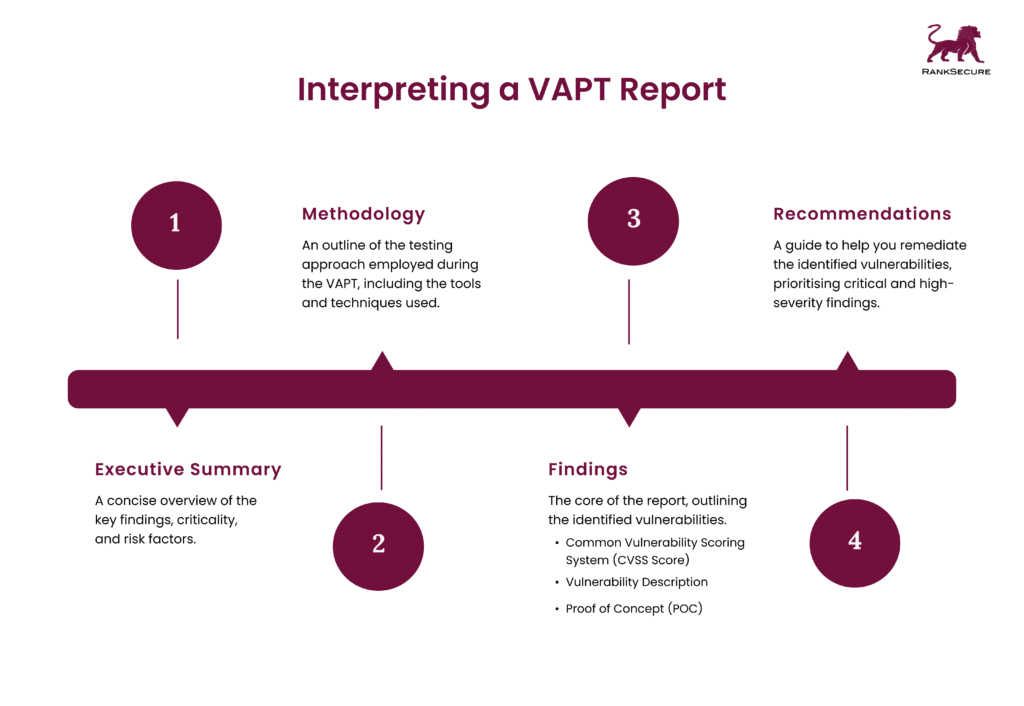
Executive Summary
This is a concise overview summarising the key findings, including the criticality of vulnerabilities and the overall security posture of your application.
Methodology
This section outlines the testing approach employed during the VAPT, including the tools and techniques utilised.
Findings
This section constitutes the core of the report, precisely outlining the identified vulnerabilities. It categorises these vulnerabilities by:
CVSS Score: The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) assigns a severity score (critical, high, medium, low) to each vulnerability, aiding in their prioritisation.
💡 CVSS is an open framework maintained by the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST), a US-based nonprofit with over 500 member organisations globally. It is derived from scores in the three groups – Base, Temporal, and Environmental – that cover the different characteristics of a vulnerability, including its impact and environmental endurance over time.Vulnerability Description: This is a comprehensive explanation of the vulnerability, including its technical details and potential impact on your application.
Proof of Concept (POC): In some cases, the report might include a Proof of Concept (POC) demonstrating how a malicious actor could exploit the vulnerability.
Recommendations
This section guides you in remediating the identified vulnerabilities, often prioritising critical and high-severity findings. The recommendations might involve patching software, code modifications, or security configuration adjustments.
Interpreting the Findings
When analysing a VAPT report, you must prioritise vulnerabilities based on their CVSS score. Critical and high-severity issues pose the most significant risk to your organisation and warrant immediate attention. Here’s a breakdown of the CVSS score interpretations:
Critical (CVSS Score: 7.0 – 10.0):
These vulnerabilities can be effortlessly exploited, potentially resulting in complete system compromise or data breaches.
High (CVSS Score: 4.0 – 6.9): These vulnerabilities can be exploited with moderate effort, leading to significant security consequences.
Medium (CVSS Score: 2.0 – 3.9):
Exploiting these vulnerabilities requires specific conditions, but they can still cause damage.
Low (CVSS Score: 0.0 – 1.9):
These vulnerabilities are difficult to exploit and often have minimal impact.
Acting On The Results of a VAPT Assessment
Once you have grasped the vulnerabilities and their severity levels, it is time to translate the report’s recommendations into concrete actions. Here’s a recommended approach:
Prioritising Remediation
Categorising vulnerabilities
To ensure that your resources are allocated efficiently, you must begin by focussing on remediating critical and high-severity vulnerabilities first.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
To strengthen your organisation’s defences effectively, you must connect technical vulnerabilities with real-world business impact. A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) helps you evaluate the potential consequences of each vulnerability on your organisation’s operations, reputation and overall business continuity. This process also helps to align your actions with business priorities. It ensures that you are not only fixing vulnerabilities but also fortifying the areas that matter most to your organisation.
Developing A Remediation Plan
Developing an elaborate plan of action
To effectively address vulnerabilities identified through VAPT, you must craft a comprehensive remediation plan. This involves:
Delegating tasks and responsibilities: You must assign specific roles and responsibilities to team members involved in the remediation process. You must ensure that each individual understands their role and the specific tasks assigned to them. This can promote accountability and streamline the remediation process.
Establishing deadlines for resolution: You must set realistic deadlines for fixing identified vulnerabilities. Clear timelines can help to prioritise and complete the remediation process promptly. You must also strike a balance between urgency and thoroughness in resolving vulnerabilities.
Integrating patch management
This step involves executing effective patch management for successful vulnerability remediation.
Identifying available patches: You must regularly monitor vendor updates and security advisories for patches that apply to your organisatio’s software and systems. Staying proactive and informed about the latest security patches can ensure that no critical updates are overlooked.
Executing a patch deployment strategy: You must develop a well-defined strategy for deploying patches promptly and efficiently. You must prioritise patches based on how critical they are and how they might affect your organisation’s security. This also includes testing patches in a controlled environment before deployment to avoid unforeseen issues during the process.
Testing And Validation
Post-remediation testing
Once you have identified the vulnerabilities and applied the patches, it is important to conduct post-remediation testing to ensure that the implemented fixes are effective and have not introduced new issues. This ensures that the security measures you have put in place are indeed providing the intended protection.
Verifying the efficacy of patches: At this step, you must employ rigorous testing to confirm that the deployed patches have successfully closed the identified vulnerabilities. This includes simulated attacks and penetration testing to see how well your systems hold up against different threats. Doing this helps to gain confidence that the vulnerabilities have been adequately addressed, providing a higher level of security.
Reviewing VAPT to ensure resolution: Post-remediation testing does not mark the end of the VAPT process. You need to revisit testing procedures to make sure the fixes are still working well over time. This approach can help your organisation adapt to changing threats and assure your stakeholders that your systems stay secure even after the first fixes.
Continuous monitoring
Implementing security measures is not a one-time task; it is an ongoing commitment. Therefore, you should adopt a proactive strategy to regularly and systematically monitor your systems to identify and address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Implementing continuous security checks: This step involves the regular scanning of your organisation’s systems for vulnerabilities and potential threats. You can utilise automated tools to help with routine checks, however, human oversight is equally critical. This ensures that any emerging threat, that automated tools might overlook, is detected, leading to a more comprehensive security posture.
Addressing new vulnerabilities as they emerge: With new vulnerabilities emerging regularly, you must have a system to quickly address them. This involves staying updated on the latest security threats, applying patches promptly, and adjusting security measures as risks evolve. Employee training is key here, as a well-informed workforce can help by identifying and reporting potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Employee training and awareness in enhancing VAPT results: A crucial part of successful VAPT is making sure your employees are well-versed in cybersecurity best practices. They are often the first line of defence against potential threats, therefore, their awareness and understanding of security protocols can significantly contribute to your organisation’s overall digital infrastructure resilience.
Therefore, understanding the nuances of VAPT results, prioritising vulnerabilities effectively, and taking proactive steps to remediate security issues are crucial in strengthening your organisation’s security stance. As threats evolve, ongoing VAPT assessments remain critical in staying ahead of emerging vulnerabilities and ensuring the long-term resilience of your organisation’s web applications. Eventually, by embracing a proactive approach to VAPT, your organisation can not only protect its assets but also uphold the trust and confidence of its stakeholders in an increasingly interconnected digital world.
